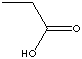
| PROPIONIC ACID
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 79-09-4, 784139-72-6 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 201-176-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | CH3CH2COOH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 74.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | 2915.50.1000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 2600 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Hydroacrylic acid; Carboxyethane; Methylacetic acid; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C-3 Acid; Metacetonic acid; Pseudoacetic acid; Ethylformic Acid; Ethanecarboxylic Acid; Acide Propionique; Kyselina Propionova; Propanyl acid; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | C(=O)(CC)O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Fungicide, Bactericide, Preservative, Acidifying agent | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTRA NOTES |
UN1848 [Corrosive] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | - 21 - - 20 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
140.7 - 141.7 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.990 - 0.998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
miscible |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
soluble in almost conventional organic solvents and alcohol. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
485 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pKa | 4.875 (at 25 C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| log P | 0.33 (Octanol-water) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR PRESSURE | 3.53 (mmHg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HENRY LAW CONSTANT | 4.45E-07 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OH RATE CONSTANT | 1.22E-12 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 3; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
50 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Light sensitive. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Local: Propionic acid is a clear, colorless liquid with a slightly sweetish odor. It is soluble in water and alcohol; melts at -21 C, boils at 141 C. It is used as a preservative in feed and food industry directly or in the forms of ammonium propionate, calcium and sodium propionates. It is used to manufacture various propionates which used in the production of pharmaceuticals, antifungal agents, agrochemicals, plastics, plasticizers, rubber chemicals, dyes, artificial flavors and perfumery synthetics. It is used also as a solvent and in nickel-electroplating solutions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASSAY (GC) |
99.5% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
0.1% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COLOR, APHA |
20 max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | 1848 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34, Safety Phrases: 9-16-23-33-36-45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CARBOXYLIC ACID |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carboxylic acid is an organic compound whose molecules contain carboxyl group
and have the condensed chemical formula R-C(=O)-OH in which a carbon atom is
bonded to an oxygen atom by a solid bond and to a hydroxyl group by a single
bond), where R is a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group. Carboxylic
acids can be synthesized if aldehyde is oxidized. Aldehyde can be obtained by
oxidation of primary alcohol. Accordingly, carboxylic acid can be obtained by
complete oxidation of primary alcohol. A variety of Carboxylic acids are
abundant in nature and many carboxylic acids have their own trivial names.
Examples are shown in table. In substitutive nomenclature, their names are
formed by adding -oic acid' as the suffix to the name of the parent compound.
The first character of carboxylic acid is acidity due to dissociation into H+
cations and RCOO- anions in aqueous solution. The two oxygen atoms are
electronegatively charged and the hydrogen of a carboxyl group can be easily
removed. The presence of electronegative groups next to the carboxylic group
increases the acidity. For example, trichloroacetic acid is a stronger acid than
acetic acid. Carboxylic acid is useful as a parent material to prepare many
chemical derivatives due to the weak acidity of the hydroxyl hydrogen or due to
the difference in electronegativity between carbon and oxygen. The easy
dissociation of the hydroxyl oxygen-hydrogen provide reactions to form an ester
with an alcohol and to form a water-soluble salt with an alkali. Almost infinite
esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between
carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. The second
reaction theory is the addition of electrons to the electron-deficient carbon
atom of the carboxyl group. One more theory is decarboxylation (removal of
carbon dioxide form carboxyl group). Carboxylic acids are used to synthesize
acyl halides and acid anhydrides which are generally not target compounds. They
are used as intermediates for the synthesis esters and amides, important
derivatives from carboxylic acid in biochemistry as well as in industrial
fields. There are almost
infinite esters obtained from carboxylic
acids. Esters
are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol. Carboxylic acid
esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain
esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and
coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking
fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting
agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates
for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters
provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling
point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application
selections. Amides
are formed from the reaction of a carboxylic acids with an amine.
Carboxylic
acid's reaction to link amino acids is wide in nature to form proteins (amide), the
principal constituents of the protoplasm of all cells. Polyamide is a polymer
containing repeated amide groups such as various kinds of nylon and
polyacrylamides. Carboxylic acid
are in our lives.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||